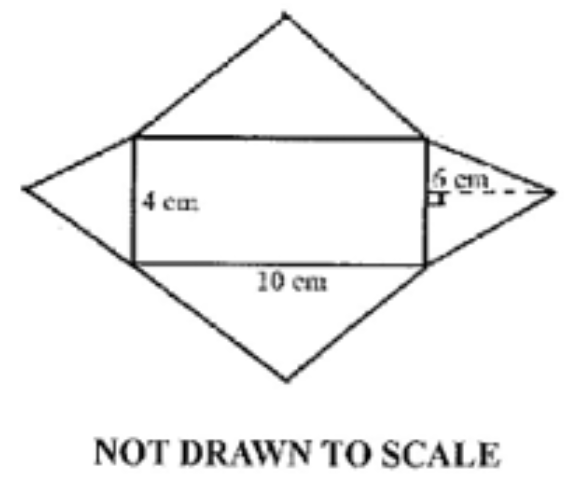
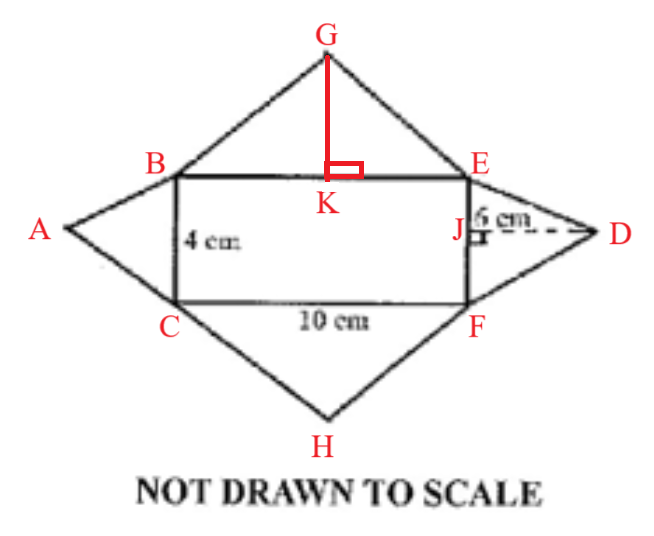
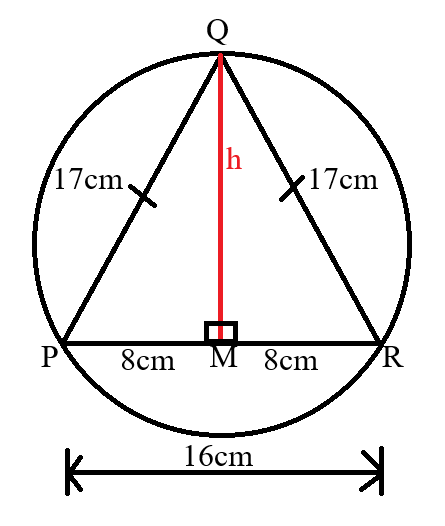
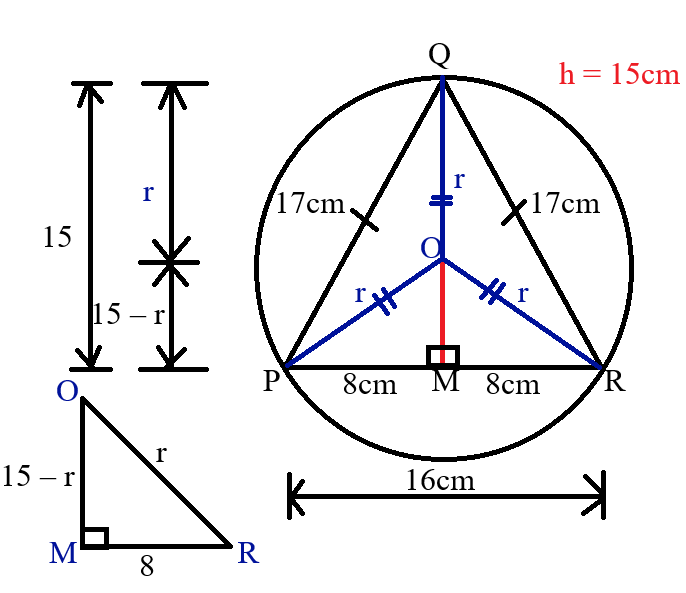
Mensuration
Welcome to Our Site
I greet you this day,
These are the solutions to WASSCE Mathematics questions on Mensuration.
If you find these resources valuable/helpful, please consider making a donation:
Cash App: $ExamsSuccess or
cash.app/ExamsSuccess
PayPal: @ExamsSuccess or
PayPal.me/ExamsSuccess
Google charges me for the hosting of this website and my other
educational websites. It does not host any of the websites for free.
Besides, I spend a lot of time to type the questions and the solutions well.
As you probably know, I provide clear explanations on the solutions.
Your donation is appreciated.
Comments, ideas, areas of improvement, questions, and constructive criticisms are welcome.
Feel free to contact me. Please be positive in your message.
I wish you the best.
Thank you.
Formulas
Right Triangle
$ perpendicular\:\:height = height \\[3ex] Area = \dfrac{1}{2} * base * height \\[5ex] height = \dfrac{2 * Area}{base} \\[5ex] base = \dfrac{2 * Area}{height} \\[5ex] hypotenuse^2 = height^2 + base^2...Pythagorean\:\:Theorem \\[3ex] hypotenuse = \sqrt{height^2 + base^2} \\[3ex] height = \sqrt{hypotenuse^2 - base^2} \\[3ex] base = \sqrt{hypotenuse^2 - height^2} \\[3ex] Perimeter = hypotenuse + height + base \\[3ex] Area = \dfrac{1}{2} * height * base * \sin (hypotenuseAngle) \\[5ex] Area = \dfrac{1}{2} * height * hypotenuse * \sin (baseAngle) \\[5ex] Area = \dfrac{1}{2} * base * hypotenuse * \sin (heightAngle) \\[5ex] Semiperimeter = \dfrac{height + base + hypotenuse}{2} \\[5ex] Semiperimeter - height = firstdifference \\[3ex] Semiperimeter - base = seconddifference \\[3ex] Semiperimeter - hypotenuse = thirddifference \\[3ex] Area = \sqrt{Semiperimeter * firstdifference * seconddifference * thirddifference}...Hero's\:\:Formula\:\:or\:\:Heron's\:\:Formula \\[5ex] hypotenuse = {Perimeter^2 - 4 * Area}{2 * Perimeter} \\[5ex] base = \dfrac{(Perimeter - hypotenuse) \pm Math.sqrt((hypotenuse - Perimeter)^2 - 8 * Area)}{2} \\[5ex] height = \dfrac{2 * Area}{base} $
Triangle
$ Perimeter = firstside + secondside + thirdside \\[5ex] Area = \dfrac{1}{2} * firstside * secondside * \sin (thirdAngle) \\[5ex] Area = \dfrac{1}{2} * firstside * thirdside * \sin (secondAngle) \\[5ex] Area = \dfrac{1}{2} * secondside * thirdside * \sin (firstAngle) \\[5ex] Semiperimeter = \dfrac{firstside + secondside + thirdside}{2} \\[5ex] Semiperimeter - firstside = firstdifference \\[3ex] Semiperimeter - secondside = seconddifference \\[3ex] Semiperimeter - thirdside = thirddifference \\[3ex] Area = \sqrt{Semiperimeter * firstdifference * seconddifference * thirddifference}...Hero's\:\:Formula\:\:or\:\:Heron's\:\:Formula \\[5ex] \underline{Cosine\:\:Law} \\[3ex] firstside^2 = secondside^2 + thirdside^2 - 2 * secondside * thirdside * \cos (firstAngle) \\[3ex] secondside^2 = firstside^2 + thirdside^2 - 2 * firstside * thirdside * \cos (secondAngle) \\[3ex] thirdside^2 = firstside^2 + secondside^2 - 2 * firstside * secondside * \cos (thirdAngle) \\[5ex] firstAngle = \cos^{-1} \left(\dfrac{secondside^2 + thirdside^2 - firstside^2}{2 * secondside * thirdside}\right) \\[5ex] secondAngle = \cos^{-1} \left(\dfrac{firstside^2 + thirdside^2 - secondside^2}{2 * firstside * thirdside}\right) \\[5ex] thirdAngle = \cos^{-1} \left(\dfrac{firstside^2 + secondside^2 - thirdside^2}{2 * firstside * secondside}\right) \\[7ex] \underline{\text{Area of a Triangle given the vertices}} \\[3ex] \text{Let the vertices be:} \\[3ex] Vertex\;1:\;\;(x_1, y_1) \\[4ex] Vertex\;2:\;\;(x_2, y_2) \\[4ex] Vertex\;3:\;\;(x_3, y_3) \\[4ex] Area = \dfrac{1}{2}|x_1(y_2 - y_3) + x_2(y_3 - y_1) + x_3(y_1 - y_2)| $
Insribed Triangle (Circumscribed Circle)
$ Circumradius = \dfrac{firstside \cdot secondside \cdot thirdside}{4 \cdot Area} $
Square
$ side = length = width = height \\[3ex] Area = side^2 \\[3ex] side = \sqrt{Area} \\[3ex] Perimeter = 4 * side \\[3ex] side = \dfrac{Perimeter}{4} \\[5ex] diagonal = side * \sqrt{2} \\[3ex] side = \dfrac{diagonal * \sqrt{2}}{2} \\[5ex] Area = \dfrac{Perimeter^2}{16} \\[5ex] Perimeter = 4 * \sqrt{Area} \\[3ex] Area = \dfrac{diagonal^2}{2} \\[5ex] diagonal = \sqrt{2 * Area} \\[3ex] Perimeter = 2 * diagonal * \sqrt{2} \\[3ex] diagonal = \dfrac{Perimeter * \sqrt{2}}{4} $
Rectangle
$ Area = length * width \\[3ex] length = \dfrac{Area}{width} \\[5ex] width = \dfrac{Area}{length} \\[5ex] Area = \dfrac{(length * Perimeter) - (2 * length^2)}{2} \\[5ex] Area = \dfrac{(width * Perimeter) - (2 * width^2)}{2} \\[5ex] Perimeter = 2(length + width) \\[3ex] length = \dfrac{Perimeter - 2 * width}{2} \\[5ex] width = \dfrac{Perimeter - 2 * length}{2} \\[5ex] Perimeter = \dfrac{2(length^2 + Area)}{length} \\[5ex] Perimeter = \dfrac{2(width^2 + Area)}{width} \\[5ex] diagonal = \sqrt{length^2 + width^2} \\[4ex] length = \sqrt{diagonal^2 - width^2} \\[4ex] width = \sqrt{diagonal^2 - length^2} \\[4ex] diagonal = \dfrac{\sqrt{length^4 + Area^2}}{length} \\[5ex] diagonal = \dfrac{\sqrt{width^4 + Area^2}}{width} \\[5ex] diagonal = \dfrac{\sqrt{(Perimeter^2) + (5 * length^2) - (4 * Perimeter * length)}}{2} \\[5ex] diagonal = \dfrac{\sqrt{(Perimeter^2) + (5 * width^2) - (4 * Perimeter * width)}}{2} $
Circle
$ Area = A \\[3ex] Circumference = C \\[3ex] Radius = r \\[3ex] Diameter = d \\[3ex] d = 2r \\[3ex] r = \dfrac{d}{2} \\[5ex] A = \pi r^2 \\[3ex] A = \dfrac{\pi d^2}{4} \\[5ex] C = 2\pi r \\[3ex] C = \pi d \\[3ex] r = \dfrac{\sqrt{A\pi}}{\pi} \\[5ex] r = \dfrac{C}{2\pi} \\[5ex] d = \dfrac{2\sqrt{A\pi}}{\pi} \\[5ex] r = \dfrac{C}{\pi} \\[5ex] A = \dfrac{C^2}{4\pi} \\[5ex] C = 2\sqrt{A\pi} $
Cube
6 square faces
12 edges
$
edge = side = length = width = height \\[3ex]
Surface\:\:Area = 6 * edge^2 \\[3ex]
edge = \sqrt{\dfrac{Surface\:\:Area}{6}} \\[5ex]
Volume = edge^3 \\[3ex]
edge = \sqrt[3]{Volume} \\[3ex]
Volume = \dfrac{edge * Surface\:\: Area}{6} \\[5ex]
edge = \dfrac{6 * Volume}{Surface\:\:Area} \\[5ex]
Surface\:\:Area = \dfrac{6 * Volume}{edge} \\[5ex]
Volume = \dfrac{Surface\:\:Area * \sqrt{6 * Surface\:\:Area}}{36} \\[5ex]
edge = \dfrac{diagonal * \sqrt{3}}{3} \\[5ex]
diagonal = \sqrt{3} * edge \\[3ex]
Surface\:\:Area = 2 * diagonal^2 \\[3ex]
diagonal = \dfrac{\sqrt{2 * Surface\:\:Area}}{2} \\[5ex]
Volume = \dfrac{diagonal^3 * \sqrt{3}}{9} \\[5ex]
diagonal = \sqrt{3} * \sqrt[3]{Volume}
$
Cuboid (Right Rectangular Prism)
$ Volume = Length \cdot Width \cdot Height \\[3ex] $
Right Cone
Curved Surface Area = Lateral Surface Area
Height = Perpendicular Height
$
Volume\:\:of\:\:Cone = \dfrac{1}{3} * Volume\:\:of\:\:Cylinder \\[5ex]
Lateral\:\:Surface\:\:Area = LSA \\[3ex]
Base\:\:Area = BA \\[3ex]
Total\:\:Surface\:\:Area = TSA \\[3ex]
Volume = V \\[3ex]
Diameter = d \\[3ex]
Radius = r \\[3ex]
Height = h \\[3ex]
Slant Height = l \\[3ex]
r = \dfrac{d}{2} \\[5ex]
d = 2r \\[3ex]
l = \sqrt{h^2 + r^2} \\[3ex]
l = \dfrac{\sqrt{4h^2 + d^2}}{2} \\[5ex]
h = \sqrt{l^2 - r^2} \\[3ex]
h = \dfrac{\sqrt{4l^2 - d^2}}{2} \\[5ex]
r = \sqrt{l^2 - h^2} \\[3ex]
d = 2 * \sqrt{l^2 - h^2} \\[3ex]
BA = \pi r^2 \\[3ex]
r = \dfrac{\sqrt{BA * \pi}}{\pi} \\[5ex]
BA = \dfrac{\pi d^2}{4} \\[5ex]
d = \dfrac{2\sqrt{BA * \pi}}{\pi} \\[5ex]
LSA = \pi rl \\[3ex]
LSA = \dfrac{\pi dl}{2} \\[5ex]
l = \dfrac{LSA}{\pi r} \\[5ex]
LSA = \pi r\sqrt{h^2 + r^2} \\[3ex]
h = \dfrac{\sqrt{LSA^2 - \pi^2 r^4}}{\pi r} \\[5ex]
TSA = BA + LSA \\[3ex]
TSA = \pi r(r + l) \\[3ex]
l = \dfrac{TSA - \pi r^2}{\pi r} \\[5ex]
TSA = \dfrac{\pi d(d + 2l)}{4} \\[5ex]
l = \dfrac{4 * TSA - \pi d^2}{2\pi d} \\[5ex]
r = \dfrac{-\pi l \pm \sqrt{\pi^2 l^2 + 4\pi * TSA}}{2\pi} \\[5ex]
TSA = \pi r(r + \sqrt{h^2 + r^2}) \\[3ex]
h = \dfrac{\sqrt{TSA(TSA - 2\pi r^2)}}{\pi r} \\[5ex]
V = \dfrac{BA * h}{3} \\[5ex]
V = \dfrac{\pi r^2h}{3} \\[5ex]
V = \dfrac{\pi hd^2}{12} \\[5ex]
V = \dfrac{\pi h(l^2 - h^2)}{3} \\[5ex]
h = \dfrac{3V}{\pi r^2} \\[5ex]
r = \dfrac{\sqrt{3V\pi h}}{\pi h}
$
Right Cylinder
Curved Surface Area = Lateral Surface Area
Height = Perpendicular Height
$
Volume\:\:of\:\:Cylinder = 3 * Volume\:\:of\:\:Cone \\[3ex]
Lateral\:\:Surface\:\:Area = LSA \\[3ex]
Base\:\:Area = BA \\[3ex]
Total\:\:Surface\:\:Area = TSA \\[3ex]
Volume = V \\[3ex]
Diameter = d \\[3ex]
Radius = r \\[3ex]
Height = h \\[3ex]
r = \dfrac{d}{2} \\[5ex]
d = 2r \\[3ex]
LSA = 2\pi rh \\[3ex]
r = \dfrac{LSA}{2\pi h} \\[5ex]
h = \dfrac{LSA}{2\pi r} \\[5ex]
LSA = \pi dh \\[3ex]
h = \dfrac{LSA}{\pi d} \\[5ex]
d = \dfrac{LSA}{\pi h} \\[5ex]
BA = \pi r^2 \\[3ex]
r = \dfrac{\sqrt{\pi BA}}{\pi} \\[5ex]
r = \dfrac{1}{\pi} * \sqrt{\dfrac{\pi(TSA - 2 * LSA)}{2}} \\[5ex]
BA = \dfrac{\pi d^2}{4} \\[5ex]
d = \dfrac{2\sqrt{\pi BA}}{\pi} \\[5ex]
d = \dfrac{\sqrt{2\pi (TSA - LSA)}}{\pi} \\[5ex]
TSA = 2\pi r(r + h) \\[3ex]
h = \dfrac{TSA - 2\pi r^2}{2\pi r} \\[5ex]
r = \dfrac{-\pi h \pm \sqrt{\pi(\pi h^2 + 2 * TSA)}}{2\pi} \\[5ex]
TSA = 2BA + LSA \\[3ex]
BA = \dfrac{TSA - LSA}{2} \\[5ex]
LSA = TSA - 2BA \\[3ex]
TSA = \pi d\left(\dfrac{d + 2h}{2}\right) \\[5ex]
h = \dfrac{2 * TSA - \pi d^2}{2\pi d} \\[5ex]
d = \dfrac{-\pi h \pm \sqrt{\pi(h^2 + 2 * TSA)}}{\pi} \\[5ex]
h = \dfrac{LSA * \sqrt{\pi * BA}}{\pi * BA} \\[5ex]
h = \dfrac{LSA}{\sqrt{2\pi(TSA - LSA)}} \\[5ex]
BA = \dfrac{LSA^2}{\pi h^2} \\[5ex]
BA = \dfrac{(4 * TSA + \pi h^2) \pm h\sqrt{\pi(\pi h^2 - 8 * TSA)}}{8} \\[5ex]
LSA = h\sqrt{BA * \pi} \\[3ex]
LSA = \dfrac{-\pi h^2 \pm h\sqrt{\pi(\pi h^2 + 8 * TSA)}}{4} \\[5ex]
TSA = 2 * BA \pm h\sqrt{\pi * BA} \\[3ex]
TSA = \dfrac{LSA(2 * LSA + \pi h^2)}{\pi h^2} \\[5ex]
V = \pi r^2h \\[3ex]
r = \dfrac{2V}{LSA} \\[5ex]
d = \dfrac{4V}{LSA} \\[5ex]
r = \dfrac{\sqrt{Vh\pi}}{h\pi} \\[5ex]
V = BA * h \\[3ex]
BA = \dfrac{V}{h} \\[5ex]
h = \dfrac{V}{BA} \\[5ex]
h = \dfrac{V}{\pi r^2} \\[5ex]
h = \dfrac{4V}{\pi d^2} \\[5ex]
V = \dfrac{\pi d^2h}{4} \\[5ex]
d = \dfrac{\sqrt{Vh\pi}}2{h\pi} \\[5ex]
V = \dfrac{LSA^2}{h\pi} \\[5ex]
LSA = \sqrt{Vh\pi} \\[3ex]
h = \dfrac{LSA^2}{4V\pi} \\[5ex]
V = \dfrac{(h^3\pi + 4 * TSA * h) \pm h^2\sqrt{\pi(h^2\pi + 8 * TSA)}}{8} \\[5ex]
TSA = \dfrac{2V + h\sqrt{Vh\pi}}{h} \\[5ex]
TSA = \dfrac{2V + 2\pi rh^2}{h} \\[5ex]
r = \dfrac{TSA * h - 2V}{2\pi h^2} \\[5ex]
d = \dfrac{TSA * h - 2V}{\pi h^2} \\[5ex]
h = \dfrac{TSA \pm \sqrt{TSA^2 - 16\pi rV}}{4\pi r}
$
Trapezoid
Trapezoid's Midpoint Segment Theorem states that the line segment connecting the nonparallel sides of a
trapezoid is parallel to the bases, and it's length is the average of the lengths of the bases.
$
Midline = \dfrac{short\;\;base + long\;base}{2}
$